Most of the people whenever look towards night sky; they try
to find out the brightest star in the sky. If you also had tried the same then
you must have observed that the brightest star in the sky can be viewed only
during evening or morning. Actually the brightest object in the sky after sun
and Moon is not a star but a
planet which is Venus, the planet Mercury is also bright but fainter than Venus.
planet which is Venus, the planet Mercury is also bright but fainter than Venus.
What is morning and evening star?
The planet which has orbit smaller than the orbit of Earth
is called the inferior planet. The planet Mercury and Venus are the only
inferior planets. The Mercury and Venus both behave similarly so we will deal
with them in general as inferior planets. Because of smaller orbit of inferior
planet, they usually appear in the region around the Sun and cannot go opposite
to the Sun in the night sky. Closeness of inferior planet to the Sun forces
them to act as morning and evening stars.
In the ancient time people believes that the evening and
morning stars are different objects. When Venus was a morning star then it was
known as Phosphorus or Lucifer and when it was an evening star then it was
known as Hesperus.
Let us look in detail how does the inferior planet act as
morning and evening star?
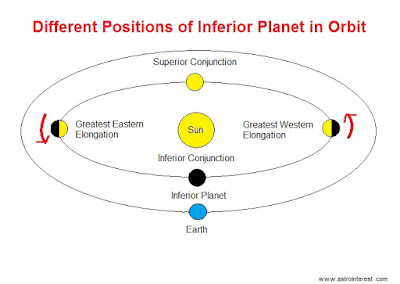
Different positions of Mercury and Venus around the Sun.
The inferior planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical
orbits and the distance of inferior planets from the Earth varies according to
the different positions in orbit.
When the inferior planet is on the opposite side of the Sun
then it is at the farthest distance from the Earth. This position is called
Superior Conjunction. At Superior Conjunction, the planet is hidden behind the
glare of the Sun and cannot be observed.
Now the inferior planet moves towards the left or towards
Eastern sky as seen from the Earth. In doing so, the separation between the
inferior planet and the Sun increases as seen from the Earth and become largest
at the position called the Greatest Eastern Elongation. At Greatest Eastern
Elongation, right or Western half of the face of inferior planet is illuminated
by the Sun as seen from the Earth.
 |
| Orbit of Inferior Planet. (Credit: Astrointerest) |
As the planet proceed on its orbit, the distance between the
inferior planet and the Sun appears to decrease and becomes zero when the
planet passes in front of the Sun. At this position, the inferior planet is at
the shortest distance from the Earth. This position is called the Inferior
Conjunction. At Inferior Conjunction, it is not necessary that planet passes
exactly in front of the Sun’s disc due to the inclination of orbit of the
inferior planet with respect to the orbit of Earth. But whenever the inferior
planet passes exactly in front of the Sun’s disc, the phenomenon is called the
transit. Otherwise the planet is completely lost in the glare of the Sun and
cannot be observed.
Now the planet moves towards the right or western sky as
seen from the Earth and the distance between the inferior planet and the Sun
appears to increase and become largest at the right most position called
Greatest Western Elongation. At Greatest Western Elongation, the left or
Eastern half of inferior planet is illuminated by the Sun as seen from the
Earth.
After this, the inferior planet again moves behind the Sun
and reaches the position of Superior Conjunction and the cycle repeats again.
After knowing about the different position, we can discuss the role of Venus
and Mercury as morning and evening stars.
Mercury and Venus as Evening Star
 |
| Venus and Mercury as Evening Stars in the Western sky. (Source: Stellarium) |
After the position of Superior Conjunction the inferior
planet moves towards the Eastern sky and reaches the Greatest Eastern
Elongation and then goes to Inferior Conjunction. During this Eastern half of
the orbit, the planet follows the Sun as Earth rotates from West to East. It
means during rotation of Earth, the Sun moves towards West and sets in the
Westerns sky in evening but the inferior planet is still behind the Sun in the
Eastward direction and it will set in the western sky after some time. So the
inferior planet will keep on glowing in the western sky in the evening after
the Sunset and known as the evening star. The highest position in the western
sky in the evening will correspond to the Greatest Eastern Elongation.
Mercury and Venus as Morning star
After the Inferior Conjunction, the inferior planet moves
towards the western sky for the position of Greatest Western Elongation and
then towards Superior Conjunction. During this Western half of the orbit, the
Sun follows the inferior planet, means as the Earth rotates the inferior planet
moves from East to West but the Sun is lagging behind in the Eastward
direction. So the inferior planet will rise in the morning in the East much
before sunrise and keep on glowing for
some time and it will lost in the day light with the sunrise. At this time the
inferior planet is known as morning star and the highest position in the eastern
sky in the morning just before sunrise will correspond to the Greatest Western
Elongation.
Observation of Venus and Mercury
As the orbit of Mercury is smaller than the orbit of Venus,
the Greatest Elongation is also smaller in case of Mercury which will result in
the smaller height of Mercury above the horizon as compared to Venus. So the
Venus can be seen much higher in the sky as compared to Mercury.
Mercury acts as Evening and Morning star much frequently as
compared to Venus because orbital period of Mercury is just 88 days as compared
to 224 days in case of Venus.
If you want to distinguish whether the morning or evening
star is Venus or Mercury, you need to look for brightness and height above the
horizon. The brightest one is Venus but the height may not be helpful each
time.
